How to ensure IT-Security
To minimize IT
risks and ensure both IT security and information security, companies need to
take a variety of measures. These measures can be implemented at different
levels.
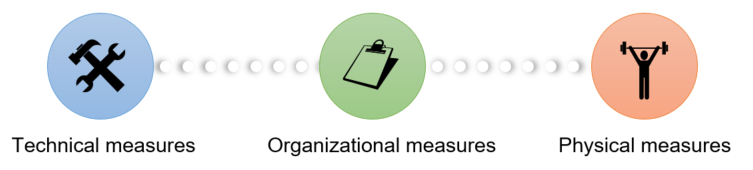
→ The measures always have to be set in relation to the security gain and the value of the systems to be protected
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1 Encryption
- Plain text is converted into cipher text
- This cryptographic text can only be
decrypted by the person authorized to do
- The conversion is done by complex
algorithms
→ The calculation only works in one direction
→ Without the key, reconstruction is not possible
When can encryption be used?
- For exchanging messages
- For secrets (of a company, e.g. product secrets)
- Encryption of personal data
- Encryption of drives
There are different methods of encryption:
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.1 Symmetric encryption
The encryption and decryption keys are the same
The communicating parties must have the same key in order to achieve communication
The transmitter has to share this key with the receiver
→ Example of an symmetric encryption algorithm: AES (Advanced Encryption Standard)
Advantages:
o Faster than asymmetric encryption
o
Ideal for large amounts of data
o
Ensures confidentiality of the data
transmitted
Disadvantages:
o
Integrity and authenticity are not
guaranteed

_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
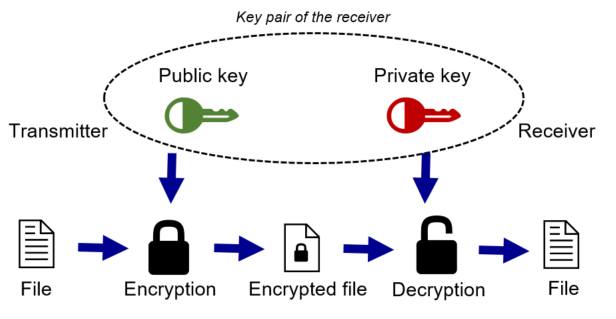
1.2 Asymmetric encryption
A pair of keys is created
o Public key (Encryption)
o Private key (Decryption)The receiver provides the public key
The transmitter wants to send something to the receiver
→ He takes the public key and encrypts his message
The receiver can use the private key to decrypt the message
→ Example of an asymmetric encryption algorithm: RSA, ECC (Elliptic Curve Cryptography)
Advantages:
o
High security
o No key needs to be exchanged secretly
as with symmetric encryption
Disadvantages:
o
Slower than symmetric encryption
→ Use cases: Mail communication, digital signatures, cryptocurrencies, public key infrastructure
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
1.3 Hybrid cryptosystem
Tina wants to send a message to Darina.
1. Darina generates a private and a public key
2. Darina sends the public key to Tina
3. Tina generates a session key for the current session
4. Tina uses the session key to encrypt the message
5. Tina encrypts the session key with Darina’s public key
6. Both (the message encrypted AND the encrypted session key) are sent to Darina as one package
7. Darina receives the package
8. Darina decrypts the session key with her private key
9. The message can be accessed with the decrypted session key
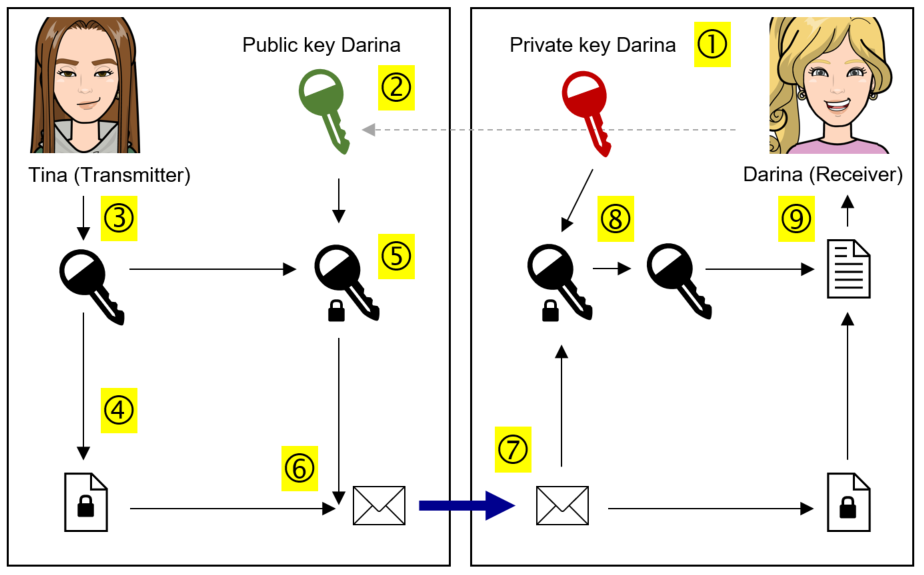
→ Uses key encapsulation (with public and private keys) and data encapsulation (with session key)
Advantages:
o
High level of security because message and
key are encrypted
Disadvantages:
o
Slow and complex
o
With large amounts of data it needs a long
time
→ Use cases: Mail
communication, IPsec


