IT-Security
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-ShareAlike 2.0 Generic License.
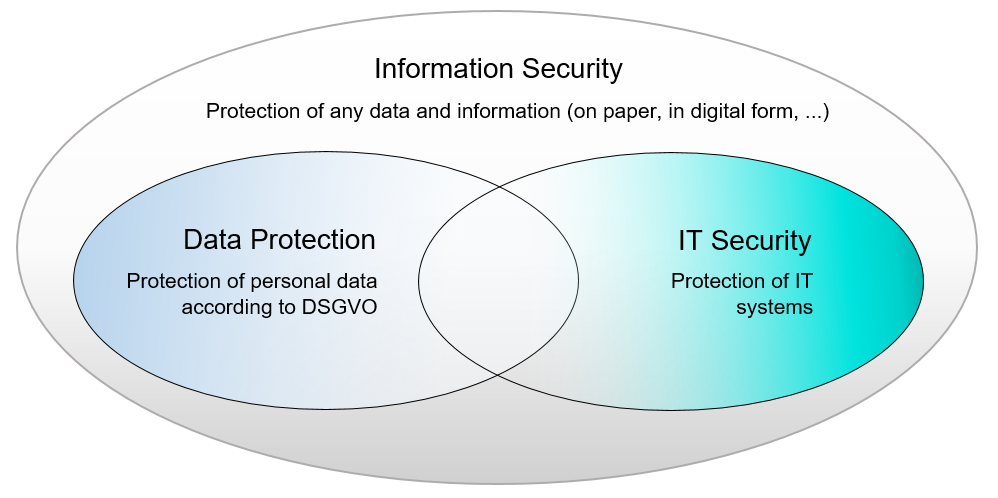
How exactly is information security realized?
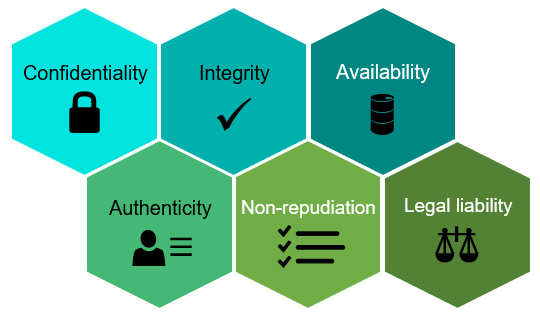

1 Confidentiality:
Refers to the
access to data
Can no unauthorized
third parties read the data?
- Only persons who
are authorized get access to the data
→During transport, storage and processing of data - Data is not modified or read by unauthorized persons
Typical measures:
> Encryption
> Data Classification Policy
»Three risk classifications: public, internal,
confidential
> Access controls (Building and room security)
> Room monitoring
> Locking offices and computers during breaks, after
regular working time and before leaving workplace
> Permission controls (Read and write permissions)
> Securing computers against theft
2 Integrity:
Refers to the data itself
Is the data unchanged and complete?
- The data is unchanged and complete
It must not be possible to change data unrecognized or unnoticed
→Data changes must be traceable
Typical measures:
> Cryptographic checksums
> Permission controls
3 Availability:
Refers to the
access to data
Is the data available to authorized persons when
needed?
- Ensures that systems and data are available
Minimizing the risk of system failures
Typical measures:
> Redundancy
> Data backups
> Important data should be stored in fire protection areas

4 Authenticity:
Refers to the
persons involved
Is the author/reader
of the data actually the person authorized?
- Verification of the origin of the data
- Verification of the author of the data
- Verification of
the reader of the data
→Especially refers to documents that are transmitted electronically - Authenticity can be checked on the basis of unique identities and characteristic properties
Typical measures:
> Authentication
» Username / Password
» Fingerprint verification
» Facial recognition (Face ID)
> Digital signature
5 Non-repudiation:
Refers to the persons involved
Is
it possible to prove that the author/reader was the author/reader even if
he/she wants to deny it?
- Ensures that all actions cannot be denied later
by the parties involved
→To guarantee the legally binding nature of transactions carried out - Legally binding nature of electronically performed business transactions, e-commerce, e-business
Typical measures:
> Digital signature
> Audit trail/log
6 Legal liability:
Is it possible to prove data and processes in a legally binding form?
- Guarantee that
data and processes can be legally proven to third parties at any time
→Transparency (traceability)
→Reversibility and prevention of false deniability
→Proof of assured properties (assurance)
→Requirement for auditability